The Health Blog

How to Reduce Inflammation for Better Health
Inflammation is a growing topic in health discussions today. While acute inflammation is a necessary immune response to injury or infection, chronic inflammation can be harmful and contribute to serious diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. Managing inflammation is essential for long-term health and well-being.
Many people mistakenly believe that inflammation is caused only by infections or injuries. Chronic inflammation often results from lifestyle choices, diet, and stress. This guide will help you understand how inflammation affects your body and provide actionable steps to reduce it through diet, exercise, stress management, and better sleep.
Key Benefits of Reducing Inflammation

Why It Matters
Lowering inflammation has benefits that extend far beyond disease prevention. It enhances overall health, energy levels, and mental clarity. Chronic inflammation is linked to fatigue, joint pain, and mood disorders. By embracing an anti-inflammatory lifestyle, you can improve your quality of life and reduce the risk of chronic illnesses.
Research shows that individuals following an anti-inflammatory diet experience a 20% reduction in heart disease risk and significant decreases in inflammatory markers. Let’s explore the best ways to achieve these benefits.
Pro Tip: Hydration Matters- Drink plenty of water to flush toxins and reduce inflammation. Herbal teas, such as ginger or green tea, are also beneficial.
Quick Guide to an Anti-Inflammatory Lifestyle

Step 1: Understanding Inflammation
To reduce inflammation, it is essential to recognise its signs and causes. Chronic inflammation can manifest as:
- Fatigue and low energy levels
- Frequent headaches or brain fog
- Joint pain or muscle stiffness
- Digestive issues, such as bloating or IBS
- Skin conditions, including eczema or acne
You can take proactive steps to lower inflammation by identifying these symptoms early.
Pro Tip: Listen to Your Body- Everyone responds differently to diet and exercise. Monitor how your body reacts and adjust accordingly.
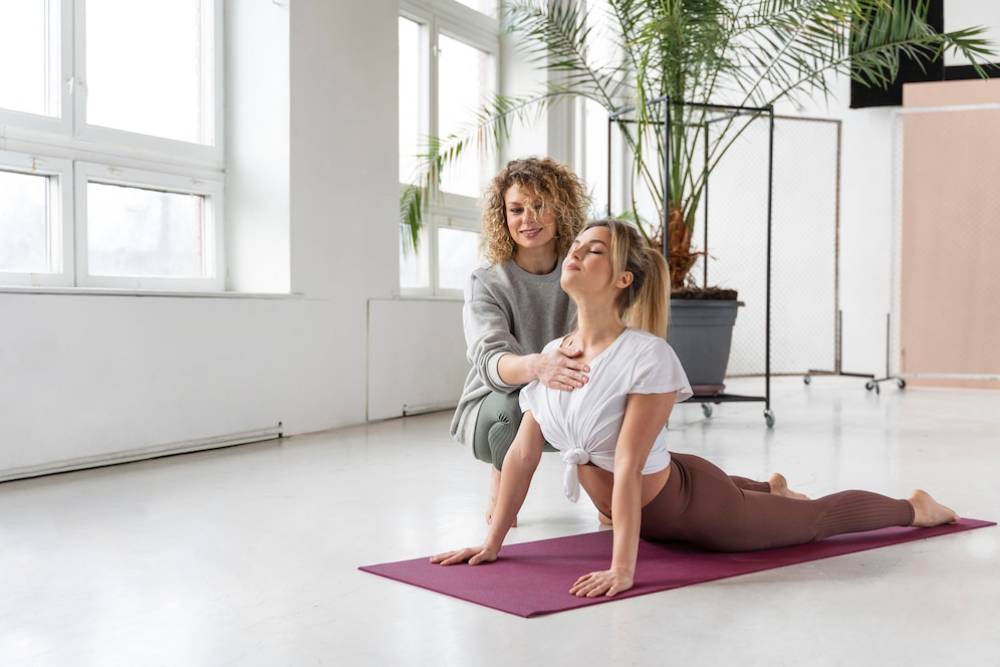
Step 2: Embrace an Anti-inflammatory Diet
Foods That Fight Inflammation
Your diet plays a significant role in managing inflammation. Incorporate the following nutrient-rich foods:
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which reduce inflammation.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard contain antioxidants that help combat inflammation.
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are rich in anthocyanins, potent anti-inflammatory compounds.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and flaxseeds provide healthy fats that reduce inflammation.
- Olive Oil: Extra virgin olive oil is known for its anti-inflammatory properties.
- Turmeric: It contains curcumin, a compound with proven anti-inflammatory effects.
Foods to Avoid
Some foods worsen inflammation and should be limited or eliminated:
- Processed meats and fried foods
- Sugary beverages and refined carbohydrates
- Excessive alcohol and trans fats
- Artificial additives and preservatives
Step 3: Incorporate Physical Activity
Regular exercise plays a crucial role in lowering inflammation. Physical activity improves circulation, reduces stress hormones, and promotes immune function. Aim for:
- 150 minutes of moderate-intensity weekly exercise (e.g., brisk walking, cycling, swimming).
- Strength training twice a week to maintain muscle health.
- Gentle activities like yoga or stretching enhance recovery and reduce tension.
Step 4: Manage Stress Effectively
Chronic stress increases inflammation.
Implement stress-reducing practices such as:
- Meditation or deep breathing exercises
- Spending time in nature
- Journaling or engaging in hobbies
- Practicing mindfulness and gratitude
Step 5: Prioritize Sleep
Lack of sleep contributes to inflammation and weakens the immune system.
To improve sleep quality:
- Stick to a consistent sleep schedule (7-9 hours per night).
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine (e.g., reading, light stretching, avoiding screens).
- Ensure your bedroom is calm, dark, and quiet for optimal rest.
Important Tip: Supplement Smartly- Consider taking omega-3s, turmeric, or probiotics to support an anti-inflammatory lifestyle.
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
Relying Solely on Medication: While medications may help, they shouldn’t replace lifestyle changes that target inflammation at its root cause.
Ignoring Mental Health: Emotional stress is a major contributor to chronic inflammation. Managing stress is just as crucial as diet and exercise.
Believing Inflammation Is Only Physical: Inflammation affects both body and mind. Addressing emotional well-being is key to reducing overall inflammation.
Advanced Insights & Expert Recommendations

Gut Health and Inflammation
Your gut microbiome plays a significant role in inflammation. To support gut health:
- Eat fermented foods (e.g., yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut).
- Increase fibre intake (e.g., legumes, vegetables, whole grains).
- Avoid excessive antibiotics and processed foods.
Herbal Remedies for Inflammation
- Ginger: Reduces muscle pain and supports digestion.
- Boswellia: A natural anti-inflammatory often used for joint health.
- Ashwagandha: Helps lower cortisol levels and reduce stress-induced inflammation.
A Healthier Life Through Reduced Inflammation
Reducing inflammation requires a multi-faceted approach, including diet, exercise, stress management, and good sleep. Small lifestyle changes now can lead to significant health benefits in the long run.
Start by identifying areas for improvement—incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, increasing physical activity, or practising mindfulness. These adjustments can have profound effects on your well-being.
Are you ready to embrace an anti-inflammatory lifestyle? Begin today and experience the benefits of reduced inflammation for a healthier future!
FAQs About Inflammation and Health
1. How long does it take to see results from an anti-inflammatory diet?
Results vary, but many people notice reduced inflammation symptoms within a few weeks of consistent dietary and lifestyle changes.
2. Can exercise increase inflammation?
Intense or excessive exercise can cause temporary inflammation, but regular moderate activity helps lower chronic inflammation over time.
3. Are all fats inflammatory?
No. Healthy fats, such as those from avocados, nuts, and fish, are anti-inflammatory. Trans fats and excessive saturated fats, however, promote inflammation.
4. Does sugar cause inflammation?
Yes, refined sugars can trigger an inflammatory response. Natural sugars from fruits, however, contain antioxidants that help combat inflammation.
5. Can I still eat meat on an anti-inflammatory diet?
Yes, but opt for lean, unprocessed meats like grass-fed beef, poultry, and fish. Avoid processed meats high in additives and preservatives.